GPU-Based Large-Scale Scientific Visualization
SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 - Course Notes
Date
December 4th, 2018Time: 2:15pm - 6:00pm
Location: Tokyo International Forum, Hall D1 (1F, D Block)
Course Speakers
Johanna Beyer, Harvard UniversityMarkus Hadwiger, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Course Description
Recent advances in image and volume acquisition as well as computational advances in simulation have led to an explosion of the amount of data that must be visualized and analyzed. Modern visualization techniques combine the parallel processing power of GPUs with out-of-core methods and data streaming to enable the interactive exploration of giga- and terabytes of image and volume data. A major enabler for interactivity is making both the computational and the visualization effort proportional to the amount of data that is actually visible on screen, decoupling it from the full data size. This leads to powerful display-aware multi-resolution techniques that enable the visualization of data of almost arbitrary size. This course consists of two major parts: An introductory part that progresses from fundamentals to modern techniques, and a more advanced part that discusses details and the current state of the art of ray-guided volume rendering, display-aware processing, and novel data structures for efficient empty space skipping of large-scale multi-modal volumes. You will learn how to develop efficient GPU data structures and large-scale visualizations, and how to implement out-of-core strategies and concepts such as virtual texturing, as well as how to use modern multi-resolution representations. These approaches reduce the GPU memory requirements of extremely large data to a working set size that fits into current GPUs. You will learn how to perform ray-casting of volume data of almost arbitrary size and how to render and process gigapixel images using scalable, display-aware techniques. We will describe custom virtual texturing architectures as well as recent hardware developments in this area. We will also describe novel deterministic and probabilistic empty space skipping methods for multi-modal volumes.Level
IntroductoryIntended Audience
We target researchers and practitioners in visualization and computer graphics that want to learn recent GPU techniques and hardware/API capabilities for implementing visualization systems that scale to very large data. The course will also be interesting for people interested in processing and rendering gigapixel images in a scalable manner.Course Prerequisites
Course participants should have a basic understanding of how GPUs work and how they are programmed using standard graphics APIs such as OpenGL or Direct3D, and a basic understanding of general-purpose GPU programming using CUDA or OpenCL.Syllabus
Introduction, Basics of Scalable Volume Visualization [60 min]
After introducing the course, I will start with outlining the main scalability issues in volume visualization of large data. I will introduce GPU-based volume visualization techniques such as GPU ray-casting and we will look at out-of-core and multi-resolution data structures such as grids and trees that allow interactive rendering of large data sets. Furthermore, we will outline some general techniques for data processing and rendering that are geared towards large volumes.Speaker
Markus Hadwiger, King Abdullah University of Science and Technologyemail: markus.hadwiger @ kaust.edu.sa
Slides
pdfBio
Markus Hadwiger is an Associate Professor in computer science and the Visual Computing Center (VCC) at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia, which he joined in 2009. He leads the High-Performance Visualization research group at VCC, where his research interests include extreme-scale visual computing and visualization, volume visualization, medical visualization, large-scale image and volume processing, multi-resolution techniques, data streaming and out-of-core processing, interactive segmentation, and GPU algorithms and architectures. He is a co-author of the book Real-Time Volume Graphics published in 2006 and has been involved in many courses and tutorials about volume rendering and visualization at ACM SIGGRAPH, ACM SIGGRAPH Asia, IEEE Visualization, and Eurographics.Scalable Volume Visualization Architectures [45 min]
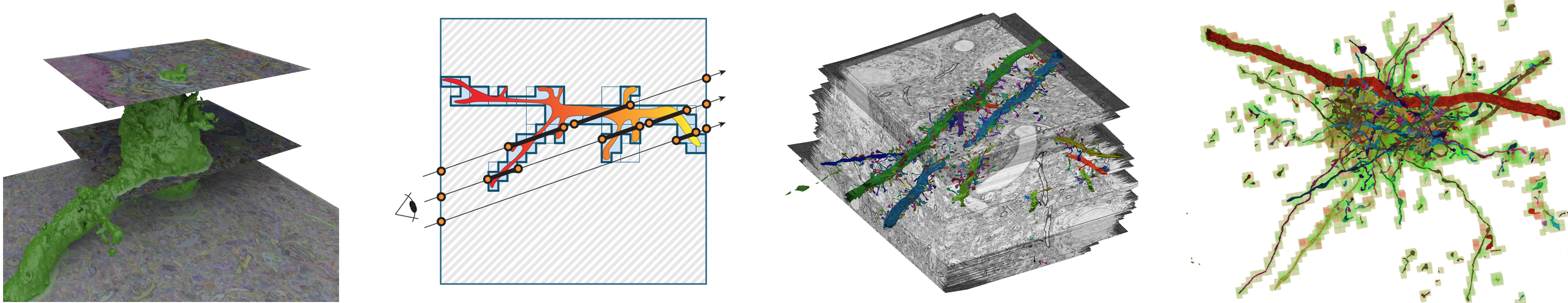
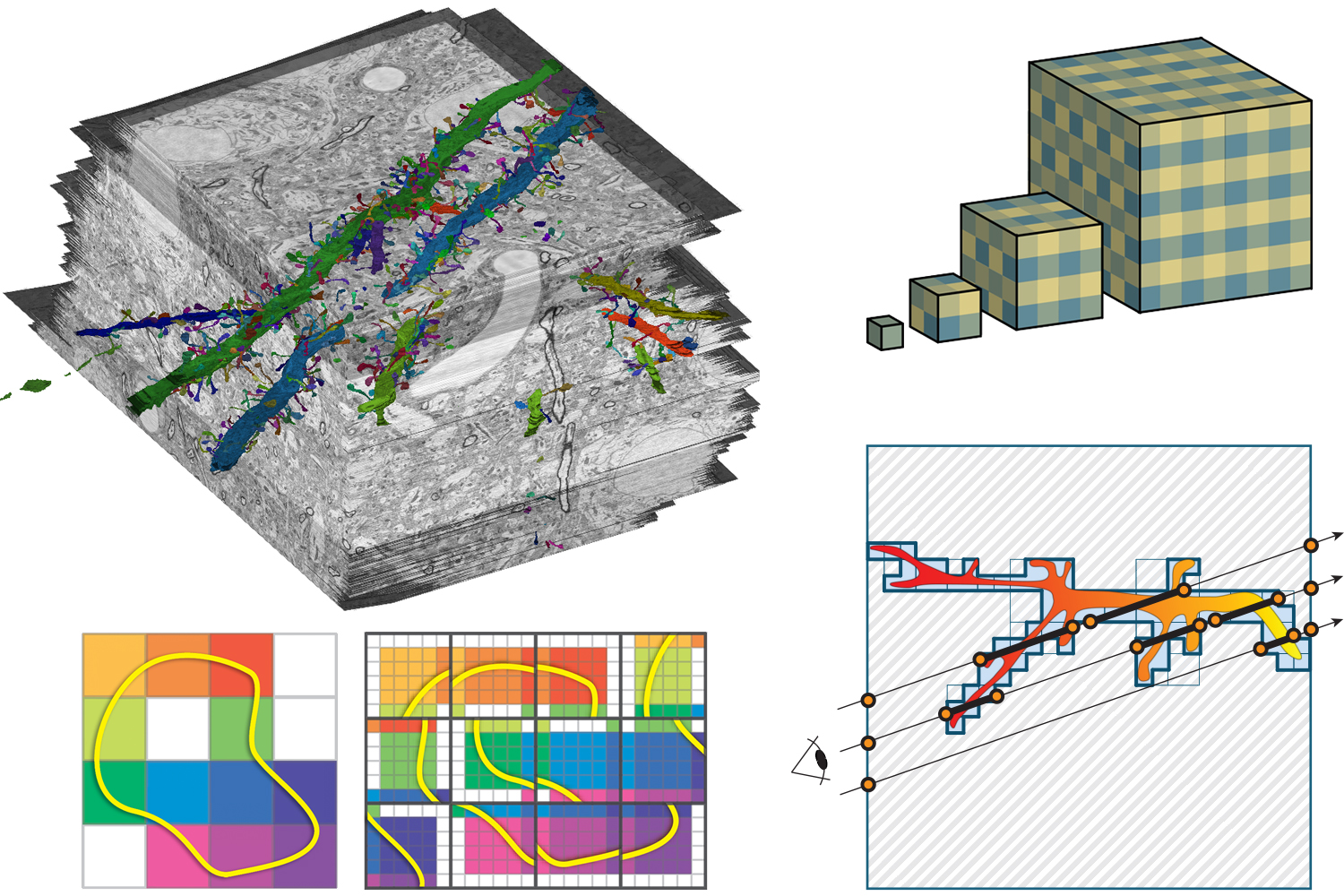 I will start by giving an overview of past and current GPU-based volume rendering algorithms. I will introduce a categorization of scalable volume rendering algorithms based on a) how the volume data is being represented in memory, b) how the active subset of the data needed for rendering (i.e., the working set) is being determined, and c) how rendering is being performed. Based on this categorization, we will analyze the scalability of today's volume visualization algorithms. Furthermore, I will give an overview of virtual texturing on GPUs and how virtual memory hierarchies can be employed for the interactive visualization of data of almost arbitrary size.
I will start by giving an overview of past and current GPU-based volume rendering algorithms. I will introduce a categorization of scalable volume rendering algorithms based on a) how the volume data is being represented in memory, b) how the active subset of the data needed for rendering (i.e., the working set) is being determined, and c) how rendering is being performed. Based on this categorization, we will analyze the scalability of today's volume visualization algorithms. Furthermore, I will give an overview of virtual texturing on GPUs and how virtual memory hierarchies can be employed for the interactive visualization of data of almost arbitrary size.
Speaker
Johanna Beyer, Harvard Universityemail: jbeyer @ seas.harvard.edu
Slides
pdfBio
Johanna Beyer is a research associate at the Visual Computing Lab at Harvard University. Before joining Harvard, she was a postdoctoral fellow at the Geometric Modeling and Scientific Visualization Center at KAUST. She received her Ph.D. in computer science at the University of Technology Vienna, Austria in 2009. Her research focuses on GPU-based volume rendering techniques for large-scale neuroscience and medical data, with emphasis on visualization of large and multimodal volumes.GPU-Based Ray-Guided Volume Rendering, and Efficient Empty Space Skipping for Large-Scale Volume Rendering [60 min]
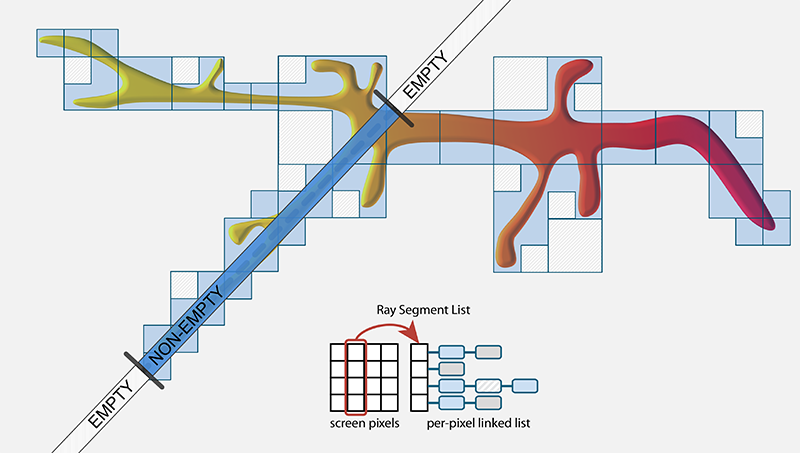
I will start by introducing current GPU-based ray-guided volume rendering algorithms, which have been demonstrated to be the most efficient approaches for interactive volume rendering of large data. We will cover ray-guided algorithms that allow to load and process data entirely on-demand, thereby limiting the amount of data that has to be handled to the visible subset on the screen. Furthermore, I will describe recent extension to these ray-guided strategies, to enable efficient empty space skipping of large datasets containing fine and intricate structures. We will cover recent methods that limit the fragmentation of space that often occurs when skipping empty regions, and present a method that supports dynamic and interactive updates of 'empty' regions. By moving the major cost of empty space skipping out of the ray-casting stage and into the faster hardware rasterization stage, empty space skipping becomes scalable than standard octree empty space skipping approaches. Finally, I will also talk about efficient deterministic and probabilistic data structures that can be used for culling and empty space skipping of large-scale segmentation volumes, and describe a hybrid deterministic and probabilistic scalable culling architecture.
Speaker
Johanna Beyer, Harvard Universityemail: jbeyer @ seas.harvard.edu
Slides
pdfDisplay-Aware Visualization and Processing [45 min]
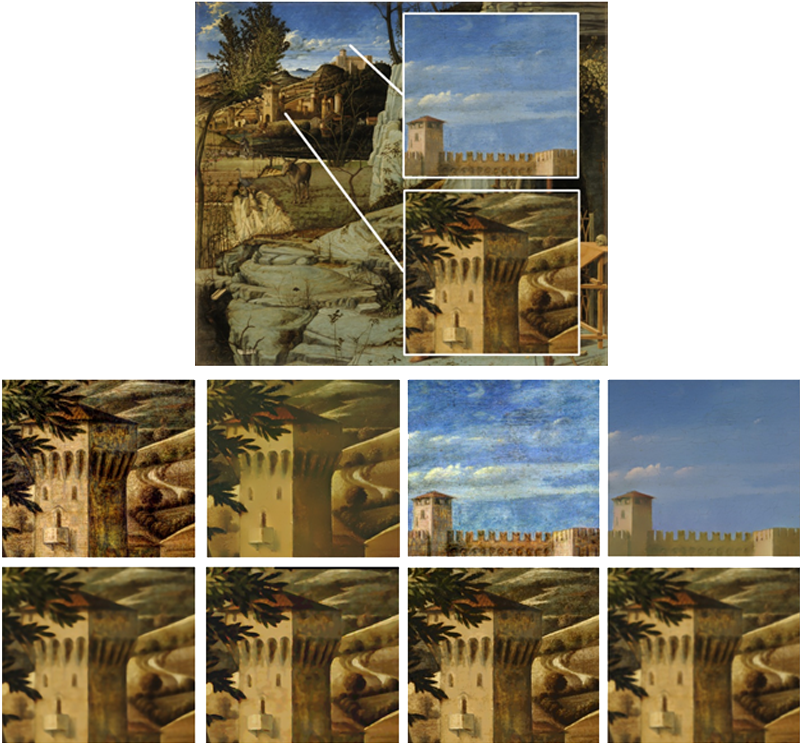 I will give an overview of display-aware techniques for the visualization and processing of gigapixel images and large-scale volume data, where the computational effort is proportional to the actually visible data instead of to the original data size. I will describe multi-resolution data structures that encode the information of high-resolution data in multi-resolution pyramids, e.g., using probability density functions of local pixel or voxel neighborhoods. This enables the accurate visualization of high-resolution data with arbitrary transfer functions at any output resolution.
I will give an overview of display-aware techniques for the visualization and processing of gigapixel images and large-scale volume data, where the computational effort is proportional to the actually visible data instead of to the original data size. I will describe multi-resolution data structures that encode the information of high-resolution data in multi-resolution pyramids, e.g., using probability density functions of local pixel or voxel neighborhoods. This enables the accurate visualization of high-resolution data with arbitrary transfer functions at any output resolution.
Speaker
Markus Hadwiger, King Abdullah University of Science and Technologyemail: markus.hadwiger @ kaust.edu.sa
Slides
pdfOutlook and Summary [15 min]
I will summarize the main concepts that were presented in the earlier sessions, and end by giving an outlook on open challenges and future directions of research for large-scale volume visualization.
Speaker
Markus Hadwiger, King Abdullah University of Science and Technologyemail: markus.hadwiger @ kaust.edu.sa